Duplex and super duplex stainless steels are advanced alloys that offer outstanding corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. These materials combine the benefits of both ferritic and austenitic stainless steels, making them ideal for use in harsh environments. Duplex stainless steels have a balanced microstructure consisting of approximately 50% ferrite and 50% austenite, while super duplex alloys feature higher molybdenum and nitrogen content, enhancing their resistance to corrosion, particularly in chloride-rich environments. Super duplex steels are especially suitable for applications requiring high strength and resistance to severe stress and corrosion, such as in the oil and gas, chemical, and marine industries.
1. Introduction to Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Duplex and super duplex stainless steels are high-performance materials designed to offer superior strength and corrosion resistance. Duplex stainless steels are characterized by a dual-phase microstructure, consisting of both ferrite and austenite. This unique structure provides an excellent combination of strength and ductility, making it ideal for various industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications. Super duplex stainless steel, a more advanced form of duplex steel, is engineered with enhanced levels of molybdenum, chromium, and nitrogen, improving its resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, making it even more suitable for demanding environments.

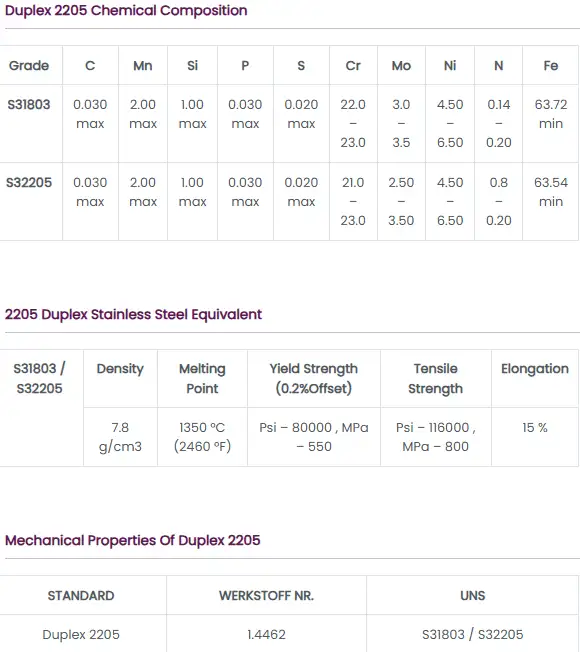
2. Composition and Microstructure of Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
Duplex Stainless Steel Composition:
-
Chromium: 18–28%
-
Nickel: 4–8%
-
Molybdenum: 1–4%
-
Nitrogen: Small quantities (typically up to 0.2%)
The microstructure of duplex stainless steels consists of roughly equal amounts of ferrite and austenite, which gives it its characteristic properties. The ferrite provides high strength, while the austenite contributes to toughness and corrosion resistance.
Super Duplex Stainless Steel Composition:
-
Chromium: 25–30%
-
Nickel: 6–9%
-
Molybdenum: 3–5%
-
Nitrogen: Up to 0.3%
The super duplex stainless steel's enhanced content of molybdenum and nitrogen results in a stronger, more corrosion-resistant alloy, making it ideal for more aggressive environments, such as those involving high chlorides.
3. Key Differences Between Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steel
| Feature | Duplex Stainless Steel | Super Duplex Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium Content | 18–28% | 25–30% |
| Nickel Content | 4–8% | 6–9% |
| Molybdenum Content | 1–4% | 3–5% |
| Nitrogen Content | Up to 0.2% | Up to 0.3% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Strength | High | Higher |
| Applications | General industrial, mild marine environments | Harsh environments, high-chloride, oil and gas, chemical industries |
4. Advantages of Duplex Stainless Steel
Duplex stainless steels offer several key advantages:
-
Cost-Effective: Compared to austenitic stainless steels, duplex alloys are more cost-effective due to their lower nickel content.
-
High Strength: Duplex alloys typically offer higher tensile strength (550-800 MPa) than austenitic stainless steels, making them ideal for structural applications.
-
Excellent Resistance to Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): Duplex steels are much less susceptible to SCC, especially in chloride-rich environments.
-
Good Fatigue Resistance: Duplex steels are designed to withstand dynamic loads, making them suitable for rotating machinery and equipment exposed to high vibrations.
5. Advantages of Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Super duplex steels offer enhanced versions of the advantages of duplex steels:
-
Superior Corrosion Resistance: The higher molybdenum and nitrogen content significantly improve pitting, crevice, and stress corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and aggressive chemical environments.
-
Higher Strength: Super duplex stainless steels offer greater tensile and yield strength than duplex alloys, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
-
Improved Durability: The superior corrosion resistance translates to a longer service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
-
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of industries, including subsea, chemical processing, and desalination plants.
6. Mechanical Properties of Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
Both duplex and super duplex stainless steels offer exceptional mechanical properties, but super duplex alloys have enhanced strength due to their higher alloy content.
| Property | Duplex Stainless Steel | Super Duplex Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 550–800 MPa | 800 MPa+ |
| Yield Strength | 400–550 MPa | 550 MPa+ |
| Elongation | 25–40% | 25–35% |
| Hardness | 200–250 HB | 250–300 HB |
7. Corrosion Resistance: Comparing Duplex and Super Duplex Alloys
Both duplex and super duplex steels are resistant to corrosion in aggressive environments, but super duplex steels excel in:
-
Chloride Environments: Super duplex steels are particularly effective in resisting corrosion from chloride ions, making them suitable for use in seawater and other chloride-heavy environments.
-
Pitting and Crevice Corrosion: Super duplex steels have a higher resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion due to their increased molybdenum and nitrogen content.
-
Stress Corrosion Cracking: Super duplex alloys are more resistant to stress corrosion cracking, which can be a concern in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
8. Applications of Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
Duplex and super duplex stainless steels are used in a variety of demanding applications:
-
Oil and Gas: For pipelines, subsea equipment, and pressure vessels exposed to harsh environments.
-
Marine: Used in shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and desalination plants.
-
Chemical Processing: Employed in reactors, heat exchangers, and storage tanks exposed to aggressive chemicals.
-
Power Generation: Ideal for components in power plants that are subject to high temperatures and corrosive environments.
9. Manufacturing and Fabrication Techniques for Duplex and Super Duplex Steels
Duplex and super duplex stainless steels are manufactured through casting, rolling, and annealing processes. These steels require careful control during fabrication to maintain their optimal mechanical properties:
-
Hot Working: The material is heated and formed into shapes like plates, sheets, or coils.
-
Cold Working: Performed to improve the mechanical properties and surface finish.
-
Annealing: Ensures a uniform microstructure and relieves internal stresses.
-
Heat Treatment: Special heat treatments are often used to maintain corrosion resistance and enhance mechanical strength.
10. Welding Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Welding duplex and super duplex stainless steels can be challenging due to the need to preserve the alloy's unique microstructure. It is critical to use the correct welding techniques and filler materials to avoid compromising the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties:
-
Preheating: Minimizes thermal shock.
-
Post-Weld Heat Treatment: Ensures proper phase balance in the alloy and enhances corrosion resistance.
11. Challenges in Using Duplex and Super Duplex Stainless Steels
-
Cost: Super duplex steels are more expensive than duplex alloys due to their higher alloy content.
-
Welding Complexity: Special care must be taken during welding to maintain optimal corrosion resistance.
-
Fabrication Difficulty: Both duplex and super duplex steels can be more difficult to fabricate compared to austenitic steels, especially in highly specialized applications.
12. Future Trends and Developments in Duplex and Super Duplex Steel
Research continues to focus on improving the corrosion resistance, weldability, and cost-effectiveness of duplex and super duplex stainless steels. Future developments may include the creation of alloys with even better performance in extreme environments, as well as advancements in fabrication techniques.
13. Global Market Overview
The demand for duplex and super duplex stainless steels continues to grow, particularly in industries such as oil and gas, marine, and chemical processing. As industries strive for longer-lasting and more reliable materials, the market for high-performance alloys is expected to expand.
14. Duplex vs. Super Duplex: Which One to Choose?
When choosing between duplex and super duplex stainless steel, the decision largely depends on the application:
-
Duplex Stainless Steel: Ideal for general industrial applications with moderate corrosion exposure.
-
Super Duplex Stainless Steel: Best suited for highly aggressive environments, such as offshore and subsea applications, where superior corrosion resistance and strength are required.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the main difference between duplex and super duplex stainless steel?
-
The main difference is that super duplex steels have higher levels of molybdenum and nitrogen, making them more corrosion-resistant and stronger than duplex steels.
-
-
Why is super duplex stainless steel more expensive than duplex?
-
Super duplex alloys have higher alloy content, including more molybdenum and nitrogen, which increases the material's cost.
-
-
Can duplex and super duplex stainless steels be welded easily?
-
Welding these materials requires specialized techniques to maintain their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, but they can be welded successfully with the right precautions.
-
-
What are the main advantages of duplex stainless steel?
-
Duplex steels offer excellent strength, resistance to stress corrosion cracking, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
-
-
What industries use duplex and super duplex stainless steels?
-
These materials are widely used in oil and gas, marine, chemical processing, power generation, and desalination industries.
-
-
How do duplex and super duplex steels perform in marine environments?
-
Both duplex and super duplex steels offer excellent resistance to seawater corrosion, but super duplex steels provide enhanced protection in chloride-heavy environments.
-
-
What is the tensile strength of duplex and super duplex stainless steel?
-
Duplex steels have a tensile strength of 550–800 MPa, while super duplex alloys can exceed 800 MPa.
-
-
What applications benefit most from super duplex stainless steel?
-
Super duplex steels are ideal for subsea pipelines, offshore oil rigs, and chemical processing equipment exposed to highly corrosive environments.
-
-
What is the welding process for duplex and super duplex stainless steels?
-
Welding requires careful heat control, appropriate filler materials, and post-weld heat treatment to preserve the material's properties.
-
-
What is the future outlook for duplex and super duplex stainless steels?
-
The market for these steels is expected to grow, driven by advancements in alloy composition and increased demand from industries requiring high-performance materials.

