Inconel 600 round bar (UNS N06600) is a high-nickel, chromium-bearing alloy noted for outstanding resistance to high-temperature oxidation, carburization and many corrosive media; it balances good strength, fabricability and long service life in elevated-temperature and aggressive chemical environments, making it an excellent choice for furnace components, heat-treat tooling, chemical process fittings and nuclear hardware. For customers who require guaranteed mill origin, fast turnaround and 100% factory pricing, MWAlloys supplies Inconel 600 round bar from China with ready stock, rapid delivery options, and full traceability.
What is Inconel 600?
Inconel 600 is a nickel-chromium-iron alloy developed for high resistance to oxidation and corrosion at elevated temperatures. Its large nickel content provides a protective, slow-forming oxide film, and the alloy retains strength well into high temperatures. It is catalogued commonly under UNS N06600 and often referred to by the trade name Inconel® (a brand of Special Metals/Allegheny-Teledyne). The alloy is available in many product forms — bar, rod, plate, tube and wire — and round bar is frequently used where turned or forged components are required.
What is Inconel 600 Round Bar used for?
Typical uses for Inconel 600 round bar include, but are not limited to:
-
High-temperature furnace hardware (thermocouple wells, retorts, muffles) owing to oxidation and carburization resistance.
-
Chemical processing components exposed to caustic or chloride environments where nickel-rich alloys resist localized corrosion.
-
Nuclear industry components (due to corrosion resistance in high-purity water and reactor environments).
-
Heat treatment tooling and fixtures where dimensional stability at elevated temperature is required.
-
Aerospace and power plant parts where intermittent high temperatures and mechanical loading are present.
These applications exploit the combination of oxidation resistance, strength retention at temperature, and reasonable machinability offered by the round bar form.
What is equivalent to Inconel 600?
Common identifiers and near-equivalents:
-
UNS: N06600.
-
Werkstoff / EN (German): 2.4816
-
Commercial equivalents sometimes referenced: generic Nickel-Chromium alloys classified as Alloy 600 / Nickel 600; caution advised — only specific mill certificates prove exact compliance.
When calling out "equivalent" grades, always confirm exact chemical limits and mechanical requirements (particularly for nuclear or ASME applications) because processing route and impurity limits may vary by mill and standard.
Chemical composition
Below is a standard limiting composition table (mass %), representative of the specification ranges commonly used for UNS N06600 / Inconel 600. Values below are typical accepted ranges; consult mill certificates for exact lot composition.
| Element | Typical range (wt.%) |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | 72.0 – 76.0 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 14.0 – 17.0 |
| Iron (Fe) | 6.0 – 10.0 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.0 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.50 |
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.15 |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤ 0.50 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.015 |
Source note: This table consolidates typical limits reported by major alloy manufacturers and technical data sheets. For contract acceptance, rely on the supplier’s certified chemical analysis.
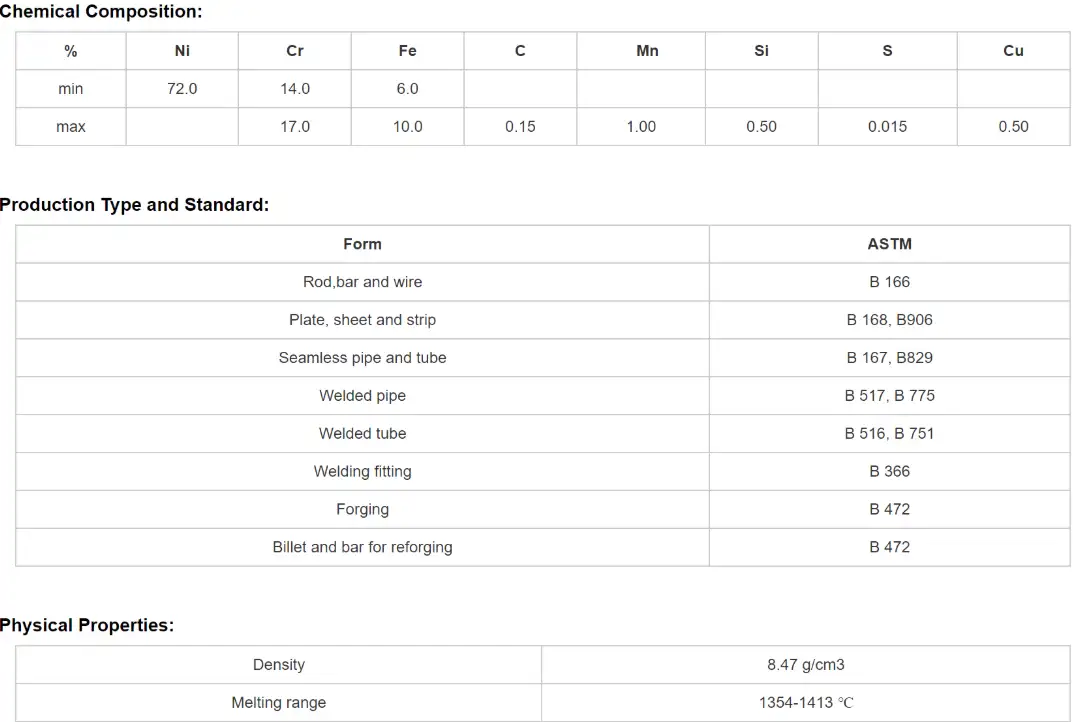
Specifications and common standards
| Application / Product form | Typical standard / spec |
|---|---|
| Round bar (general) | ASTM B166 (nickel alloy bar products) / AMS 5665 (bar) — check specific revision |
| Sheets/plate | AMS 5540 / other AMS designations |
| UNS designation | N06600 |
| EN / Werkstoff | 2.4816 |
| ASME / Pressure equipment | Compliance may be required per ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code references (refer to the specific Section/Code Case for alloy acceptance). |
Notes: standards and AMS/ASTM numbers are periodically revised; for safety-critical or nuclear procurement always quote the exact standard revision and request full mill test reports.
Mechanical properties
Typical mechanical properties for annealed Inconel 600 (product form: bar) are shown below. These are representative ranges — specification and heat treatment will affect actual values.
| Property | Typical value (annealed) |
|---|---|
| Density | ~8.47 g/cm³ |
| Tensile strength (UTS) | ~ 760 – 900 MPa (110 – 130 ksi) depending on condition |
| Yield strength (0.2% offset) | ~ 310 – 420 MPa (45 – 60 ksi) in annealed condition |
| Elongation (in 2 in) | ~ 30 – 40% (annealed) |
| Modulus of elasticity | ~ 200 GPa (typical nickel alloy region) |
| Service temperature | Useful up to ≈ 1093°C (2000°F) in some forms; long-term limits depend on environment and stress. |
Elevated temperature behavior: tensile strength remains useful at high temperature, while yield/creep resistance is moderate compared with precipitation-strengthened nickel alloys. For continuous high-stress, high-temperature components consider alloys engineered specifically for creep resistance.
What is the difference between Inconel 600 and 625?
Inconel 625 (UNS N06625) is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum-niobium alloy engineered to provide much higher tensile strength and superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion and chloride stress-corrosion cracking than 600. The principal differences:
-
Chemistry: 625 contains added molybdenum and niobium which significantly improve localized corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. 600 lacks these strengthening elements and has higher nickel content relative to certain balancing elements.
-
Strength: 625 is considerably stronger in the annealed condition (due to solid solution and precipitation hardening tendencies), making it preferred for highly stressed parts.
-
Corrosion resistance: 625 generally outperforms 600 in chloride-bearing and pitting environments, and in environments prone to stress-corrosion cracking. 600 performs well against oxidation and general corrosion but is less immune to chloride-induced localized attack.
-
Weldability and fabrication: both alloys weld and fabricate well, though filler selection and post-weld treatments vary by application.
Selection guidance: choose 600 where oxidation resistance and cost-effectiveness are priorities and chloride exposure is moderate; choose 625 where high strength and resistance to chloride pitting or crevice corrosion are critical.
Is Inconel 600 better than Stainless Steel 304?
Short answer: it depends on the application. For elevated-temperature oxidation and carburization resistance, Inconel 600 is superior. For general corrosion in mild environments and when cost is a primary factor, stainless steel 304 is often adequate and far less expensive.
Key contrasts:
-
Temperature capability: Inconel 600 retains strength and resists oxidation at much higher temperatures than 304.
-
Corrosion resistance: Inconel 600 has superior resistance in some aggressive chemical environments (esp. high-temperature oxidizing or carburizing atmospheres). 304 is good for atmospheric, food, and many aqueous applications but is prone to chloride pitting and stress-corrosion cracking at elevated temperatures relative to nickel-based alloys.
-
Cost: 304 stainless is substantially lower cost per kg and easier to source. For non-critical service at ambient temperatures, 304 is usually chosen.
Decision rule: use 304 for low-temp general service and when budget is constrained; use Inconel 600 for hot, oxidizing and chemically aggressive environments where long service life justifies higher material cost.
Fabrication, heat treatment and machining notes for round bar
-
Machinability: Inconel 600 machines more slowly than carbon steels and stainless steels. Use rigid tooling, sharp carbide inserts, positive rake angles and ample coolant to avoid work hardening.
-
Forming: The alloy is workable cold and hot; cold work increases strength at the expense of ductility. Controlled heating benefits forming operations.
-
Heat treatment: Annealing is commonly used to restore ductility — typical anneal cycles are specified in standards/heat treatment data. Stabilization (e.g., for some nickel alloys) isn’t required for Alloy 600 in the way it is for some stainless steels, but post-weld heat treatments depend on product and code requirements.
-
Welding: Generally good weldability; select proper filler metal per application and follow pre/post weld procedures for critical assemblies.
2025 Global price comparison: China, India, USA, EU
Important: metal market prices fluctuate with nickel and alloy markets, order size, form (bar vs billet), machining, and lead time. The figures below are indicative ranges gathered from contemporary supplier listings and marketplace aggregators in 2025; always request firm quotes and include freight and customs.
| Region | Typical price range (USD / kg) — Inconel 600 round bar (2025 indicative) |
|---|---|
| China (factory FOB) | US$ 22 – 30 / kg (bulk orders, factory price from manufacturers/suppliers) |
| India (domestic supplier) | US$ 28 – 38 / kg (smaller volumes, local mills/traders) |
| USA (distributor / small qty) | US$ 45 – 65 / kg (distributor stock / smaller orders; value-added cutting increases price) |
| EU (distributor) | US$ 40 – 60 / kg (depending on stock, customs, VAT) |
How to interpret: China factory prices often represent the lowest raw-material/FOB price when buying directly from mills or large manufacturers (MWAlloys partners with Chinese mills to provide 100% factory pricing). Distributor prices in the USA/EU reflect handling, certification and smaller order convenience. The market is sensitive to the nickel price; during nickel spikes, alloy prices can rise sharply.
Quality, sourcing and MWAlloys value proposition
MWAlloys (a China-based metals supplier and processor) positions itself for buyers who require:
-
100% factory origin pricing: direct sourcing from certified mills keeps margins low and price predictable.
-
Rapid stock delivery: MWAlloys maintains inventory of common diameters and lengths for quick fulfillment; standard cut-to-length and value-added machining is available.
-
Traceability and certification: full mill test reports (chemical and mechanical), material traceability and optional NDT for critical orders.
-
Customized services: threading, turning, and surface finishing supplied on request to client drawings.
If your project demands both cost control and verifiable conformity to ASTM/AMS standards, working with a supplier that can provide factory certificates and fast shipping reduces project risk. MWAlloys combines Chinese production economics with Western QA protocols to deliver both competitive pricing and documentation. (Promotional statements based on MWAlloys’ stated capabilities and typical industry practice.)
FAQs
-
Q: Can Inconel 600 be used in seawater?
A: It has reasonable resistance to general corrosion but is not the top choice for long-term seawater service where localized pitting and chloride attack occur; alloys with molybdenum (e.g., 625) or special stainless grades may be preferable. -
Q: What standard should I specify for Inconel 600 round bar?
A: Commonly ASTM B166 (bar products) and AMS specifications for aerospace/critical use; always specify the revision and required supply documentation. -
Q: Is Inconel 600 magnetic?
A: In the annealed condition, Inconel 600 is essentially non-magnetic or only weakly magnetic; cold working can impart slight magnetic response. -
Q: How to machine Inconel 600 round bar efficiently?
A: Use rigid setups, carbide tooling, lower speeds and higher feeds where possible, and ample coolant to avoid built up edge and rapid tool wear. -
Q: Can Inconel 600 be welded to stainless steel?
A: Yes, with suitable filler and procedure; consider metallurgical implications and corrosion environments to choose compatible filler metals. -
Q: What certifications are typical with bar shipments?
A: Mill Test Report (MTR / EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 where required), chemical and mechanical test certificates, and any required heat treatment records. -
Q: Is Inconel 600 suitable for cryogenic use?
A: It maintains toughness at low temperatures and is used in some cryogenic applications, though selection depends on service conditions and alternative alloys. -
Q: How does cost vary with order quantity?
A: Unit price falls significantly with larger quantities and long-term contracts; small qty orders attract distributor premiums and cutting fees. -
Q: Are there low-carbon or stabilized variants for 600?
A: Alloy 600 is available only in typical composition limits; other alloys (e.g., 601) have variations — confirm with supplier for product options. -
Q: How should I specify surface finish and tolerances for turned shafts?
A: Provide drawing tolerances and required surface finish (e.g., Ra value); discuss extra machining allowance and straightness tolerances with the supplier for accurate quoting.
Authority references
- Special Metals — INCONEL® alloy 600 technical bulletin (PDF)
- Wikipedia — Inconel (overview of nickel-chromium alloys)
- ASTM International — standards search (e.g., ASTM B166 for nickel alloy bar products)
Closing notes
If you intend to purchase Inconel 600 round bar for a critical application, include these items in your RFQ:
-
Exact specification and revision (e.g., ASTM B166, AMS number if required).
-
Required documentation (MTR EN 10204 3.1/3.2, PMI, NDT if needed).
-
Quantity, dimensions (diameter × length), tolerances and surface finish.
-
Delivery terms (FOB / CIF / DDP), lead time, and acceptance test plan.
-
Traceability and mill name (if mill origin is required by purchaser).





