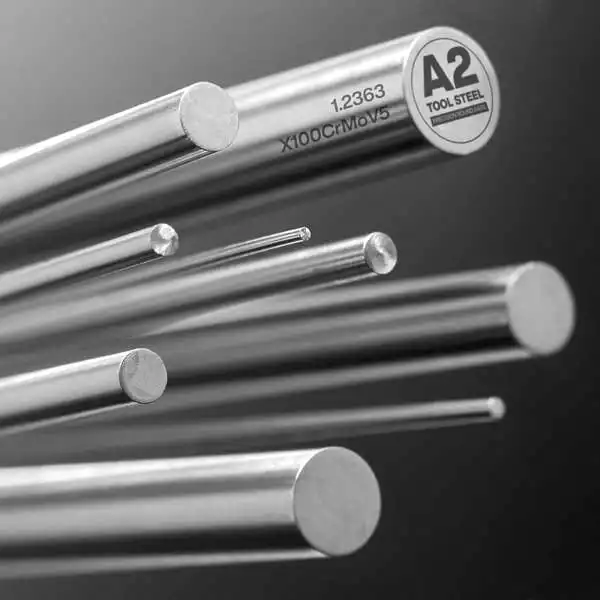
A2 tool steel (AISI A2, also referenced as DIN 1.2363 / JIS SKD12) is a versatile air-hardening cold-work grade that balances wear resistance and toughness with excellent dimensional stability during heat treatment. For most medium-run dies, punches and precision moulds where distortion control and service life matter, A2 delivers a dependable middle ground between softer oil-hardening steels and the very high wear but lower-toughness high-chromium grades. MWAlloys supplies A2 in bars, plates and ground stock from our China mill with factory pricing, fast stock dispatch and quality traceability to meet industrial and tooling customers worldwide.
What is A2 tool steel?
A2 is an air-hardening, medium alloy, cold-work tool steel primarily alloyed with chromium, molybdenum and vanadium. It was developed for tooling tasks that require good wear resistance while retaining toughness and dimensional stability after hardening. Unlike oil-quenched grades, A2 is quenched by air (or very slow gas quench) from the austenitizing temperature which reduces distortion and cracking risk in larger sections or precision components. The grade is widely used in tooling shops for medium production tools where repeatable hardness, tight tolerances and service life are required.
Quick technical snapshot
-
Group: A-series air-hardening cold work tool steel.
-
Typical hardness after tempering: 57–62 HRC (typical working range depends on tempering regime).
-
Density: ~7.86 g/cm³.
-
Primary uses: blanking and forming dies, punches, shear blades, plastic injection mould components, thread rolling dies.
-
Common supply forms: round bars, flat bars, plates, precision ground stock, hollow bars and rings.
Chemical composition (typical / nominal)
Below is a consolidated table of typical nominal composition values for A2 (AISI A2 / UNS T30102 / DIN 1.2363). Values shown are common shop/spec targets; suppliers publish narrow tolerances in certificates.
| Element | Typical range (wt%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.95 – 1.05 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 4.8 – 5.3 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.9 – 1.3 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.2 – 0.4 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.0 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.5 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.03 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.03 |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
Sources: consolidated from MatWeb typical datasheet and mill data PDFs.
Key material properties (typical, annealed and hardened)
This table summarises representative mechanical values. Actual properties depend on heat treatment, section size and manufacturing history.
| Property | Typical value (annealed or stated) |
|---|---|
| Density | 7.86 g/cm³. |
| Hardness (annealed) | ~210–250 HB (varies by finish). |
| Working hardness (hardened & tempered) | 57–62 HRC (common service range). |
| Tensile strength (approx, hardened) | ~1100 – 1400 MPa depending on HRC and temper cycle. |
| Machinability (relative) | ~35–45% of reference (free-cutting steel = 100). A2 machines acceptably in annealed state. |
| Toughness | Good; better than high chromium (D2) while offering more wear resistance than oil-hardening O1. |
| Thermal conductivity & expansion | Typical for high-carbon alloy steels; normal design allowances required for dimensional control during heat cycles. |
Specification and standards (how A2 is referenced)
A2 is covered by common tooling specifications and material trade standards. Below is a compact reference table:
| System | Common designation |
|---|---|
| AISI / SAE / UNS | A2 / UNS T30102 |
| DIN (Germany) | 1.2363 (X100CrMoV5 or similar) |
| JIS (Japan) | SKD12 (commonly comparable) |
| ASTM | A2 is a typical A-series tool steel referenced under tool steel practices; many suppliers provide material to ASTM A681 or equivalent tooling product specs. |
Manufacturing, forming and finishing processes
Forging and hot work
-
Forging temperature: warm up slowly and work in the recommended range (typical forging range 850–1100 °C). Reheat as necessary; avoid working below critical temperatures. Slow cooling and full anneal are used after forging to reduce stresses.
Machining
-
Best machined in the annealed condition. Use rigid fixturing, carbide tooling and moderate cutting speeds. When hardened, machining is very limited; grinding and EDM are primary shaping methods for finished tools. Machinability index ~40% vs mild steel.
Heat treatment (typical schedule)
A2’s heat treatment requires care for predictable hardness and minimum distortion.
Typical sequence (example)
-
Pre-heat / normalize: heat slowly to remove stresses if forged or heavily worked.
-
Austenitize: ~1020–1050 °C (temper and exact temp depend on section size and desired hardness).
-
Quench: Air quench or controlled gas quench to room temperature. For large sections a pressurised gas quench or interrupted quench gives better control.
-
Tempering: Multiple temper cycles are common to reduce retained austenite and adjust HRC to target (e.g., temper at 200–550 °C depending on desired final hardness). Typical final tempering results in 57–62 HRC.
Notes: Because A2 is air-hardening the distortion during hardening is much smaller than oil-quenched steels. This makes A2 a preferred grade for large or precision components.
Surface hardening and finishing
-
Nitriding: commonly applied to increase surface wear and improve life without drastic distortion.
-
PVD/CVD coatings: when used for plastic moulding or abrasive applications, coatings such as TiN, TiCN increase life.
-
Grinding / EDM: final sizing often uses precision grinding or EDM to meet tight tolerances.
A2 tool steel equivalents
| Country / Standard | Equivalent designation |
|---|---|
| USA / AISI | A2 (UNS T30102) |
| Germany / DIN | 1.2363, sometimes listed as X100CrMoV5 or X153CrMoV12 in narrower contexts. |
| Japan / JIS | SKD12 (commonly used comparable; check mill certificates for exact match). |
| European EN | Often referenced under cold-work tool steels (check EN standards and mill datasheets). |
Important: "Equivalent" is a functional term. Exact interchangeability requires checking the detailed chemistry, hardness, heat treatment history and application stresses. Mill certificates and sample testing are the right practice before substituting grades.
Typical uses and application notes
A2 is selected where a compromise of wear and toughness is required with controlled distortion. Common applications:
-
Blanking and forming dies (medium production runs).
-
Punches and trimming tools.
-
Shear blades and slitting knives (moderate abrasion).
-
Plastic injection mould cavities and core inserts when toughness plus dimensional stability are required.
-
Thread rolling dies, cold pilger mandrels, and cold forming tools.
Selection advice: When extreme wear life is the priority (very high abrasion), consider D2 or high chromium grades. When maximum toughness is essential, low-alloy steels or hot-work grades may be preferred. A2 often hits the optimum for mixed requirements.
Sizes and weight (typical supply forms)
A2 is supplied in many merchant sizes. Typical forms and how to estimate weight:
Common supply forms
-
Round bars — typical diameters from 6 mm up to 300 mm depending on mill.
-
Flat bars / plates — standard widths and thicknesses, e.g., 10–300 mm thick.
-
Ground flat stock — precision ground on six faces for tooling and gauges.
-
Hollow bars and rings — for specialized mandrels.
Weight calculation (example)
-
Formula: weight (kg) = volume (cm³) × density (g/cm³) / 1000
-
Example: 200 mm diameter round bar, length 1 m → volume = π × (10 cm)² × 100 cm ≈ 31,416 cm³ → weight ≈ 31,416 × 7.86 / 1000 ≈ 246.9 kg. Density used = 7.86 g/cm³.
A2 Tool Steel price comparison 2025
Important: tool steel pricing varies by quantity, product form (annealed vs ground), surface finish, certification, freight, duties and market cycles. The table below reports indicative ranges and representative sources from active 2024–2025 supplier and market pages. Use the numbers for ballpark procurement planning; request live quotes from MWAlloys for firm factory terms.
| Region | Typical retail / small order range (per kg) — 2025 indicative | Representative sources |
|---|---|---|
| USA (retail & small cuts) | ~USD 4.5 – 12.0 / kg (small cut pieces and precision ground bars are at the higher end; bulk orders lower). Examples: online distributors list per-item prices which translate to several USD/kg depending on size. | OnlineMetals, IndustrialMetalsSupply. |
| Europe (distributor / stockholder) | ~USD 3.5 – 9.0 / kg (varies by nation, VAT, and surface finish). Market indices for European steel show base steel values; tool steel premium applies. | MEPS price tables and European distributors. |
| China (mill & export bulk) | ~USD 1.5 – 4.0 / kg (large tonnage orders, annealed condition; small orders and precision ground parts higher). Alibaba and Made-in-China sourcing pages show manufacturer quotes and MOQs that imply lower mill pricing when ordered in tonnes. |
How to read this
-
Lower bound approximates FOB mill bulk shipment for industrial volumes.
-
Upper bound approximates retail/small order ground bars supplied cut to length with shipping and local margins.
-
Prices change with global raw steel cycles; check market indices (MEPS, SteelBenchmarker, ScrapMonster) and request current MWAlloys quotes.
Procurement, inspection and storage guidance
-
Mill certificates: always insist on a mill test certificate (chemical and heat treatment results) for critical tooling components.
-
Sample testing: for high-risk tools, perform hardness checks and selective destructive tests.
-
Packaging: A2 must be kept dry; oiling for long-term storage is recommended to prevent minor surface oxidation.
-
Cutting and shipping: large bars may require banding and wooden crating; declare material on shipping docs for customs and tariff classification.
-
Traceability: MWAlloys provides traceable batch numbers and inspection data on request.
MWAlloys is A2 tool steel supplier
MWAlloys supplies A2 tool steel from our China production partners with the following commercial advantages:
-
Factory pricing: direct mill prices, 100% factory FOB terms for bulk purchases.
-
Stock availability: common sizes in round, flat and ground stock ready for fast dispatch.
-
Quality checks: pre-shipment inspection, mill certificates, and option for third-party testing.
-
Customization: cutting to length, machining, and grind finishing available before shipping.
Contact MWAlloys for a tailored quote, MOQ options and delivery lead times.
FAQs
A2 Tool Steel: Air-Hardening & Dimensional Stability FAQ
1. Is A2 a stainless steel?
2. Can A2 be nitrided?
Yes. Nitriding is a common way to enhance the surface of A2 tool steel. It produces a very hard surface layer that significantly improves wear resistance and fatigue life with minimal dimensional distortion. This is ideal for mold inserts and sliding machine components.
3. What hardness can A2 reach?
Typical hardened and tempered hardness for A2 ranges from 57 to 62 HRC. The exact value depends on your specific tempering schedule and the section size of the tool. It maintains a good balance of edge retention and impact strength in this range.
4. Is A2 better than D2 for mold cores?
- Choose A2 if you need better toughness and lower distortion during heat treat. It is less likely to chip or crack under impact.
- Choose D2 if wear resistance is the primary concern for very long production runs.
Pro Tip: A2 is often favored for complex dies where dimensional precision is critical.
5. What heat treatment should be used for large dies?
6. Are there special handling rules after grinding?
7. Can you weld A2 tool steel?
8. What is the machinability of A2?
9. How to choose between A2 and H13?
The choice depends on the operating temperature. A2 is a cold-work steel designed for high hardness at room temperature. H13 is a hot-work steel designed to maintain strength and resist thermal cracking at elevated temperatures (like die casting). Never use A2 for hot-forming applications.